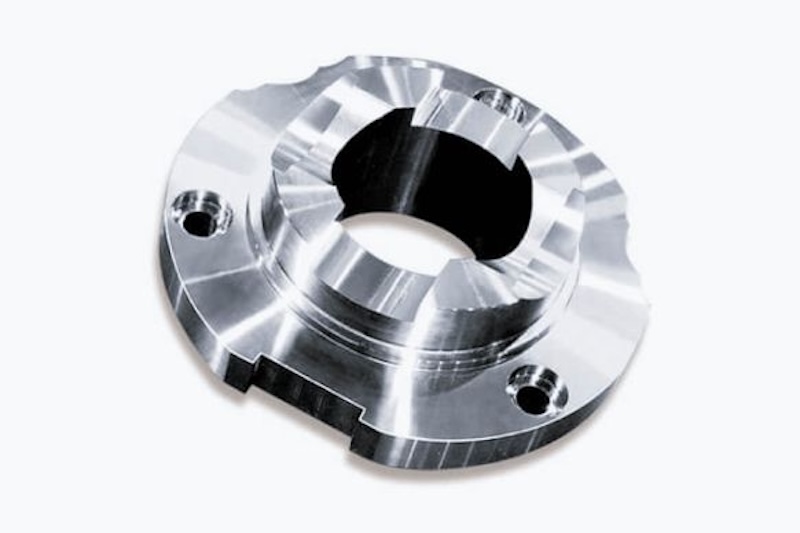
Industrial robots are bought as full methods, however beneath the housing, they’re assemblies of individually machined elements. Each joint, each actuator mount, and each end-of-arm software begins as a block of metallic on a CNC machine earlier than it turns into a part of a functioning robotic.
This issues to robotics firms as a result of the standard and lead time of those machined elements immediately have an effect on how rapidly a robotic strikes from prototype to manufacturing. A bearing housing that’s 0.05mm out of spec creates play in a joint that compounds throughout the kinematic chain.
A gearbox casing with a poor floor end wears sooner beneath load. These should not theoretical issues. They’re the sorts of points that delay product launches and drive up guarantee prices.
For firms that don’t machine elements in-house, sourcing these elements means discovering suppliers who can maintain tight tolerances within the particular supplies robotics calls for, primarily aluminum alloys, hardened steels, and typically titanium.
Online CNC machining platforms have made this simpler by permitting engineering groups to add CAD information and examine quotes from a number of verified producers, however figuring out which elements require essentially the most consideration throughout sourcing stays the engineer’s duty.
The seven elements under are current in nearly each industrial robotic. Each has particular machining necessities that have an effect on efficiency, and understanding these necessities helps each when designing for manufacturability and when evaluating potential suppliers.
1. Joint Housings
The joint housing is the structural shell that encloses the bearings, gears, and motor at every axis of rotation. It carries the complete load path between adjoining hyperlinks, so it should be stiff, dimensionally steady, and exactly bored.
Most joint housings are machined from 6061-T6 or 7075-T6 aluminum to cut back weight, although bigger industrial robots typically use ductile iron or metal castings which might be finish-machined on a CNC mill.
The crucial options are the bearing bores, which generally have to be held to inside ±0.01mm to make sure correct bearing preload and alignment. If the bore is outsized, the bearing has radial play. Whether it is undersized, the bearing seats are too tight and generate warmth beneath steady operation.
These elements nearly all the time require 4- or 5-axis milling as a result of the bearing bores, mounting faces, and cable routing options are on a number of sides of the half. A store with solely 3-axis machines will want a number of setups, rising the danger of positional error between options.
2. Gearbox Casings
Each axis on an industrial robotic has a velocity reducer, normally a harmonic drive or cycloidal gearbox, and that reducer wants a casing that maintains exact alignment between the enter and output shafts.
The casing additionally acts because the structural connection between the motor and the joint, so it should deal with each torque hundreds and the response forces from the gear mesh.
Gearbox casings are usually machined from aluminum or metal, relying on the load class. The bore that seats the wave generator or eccentric cam wants floor finishes under Ra 0.8µm and concentricity inside a couple of microns of the output bearing bore.
If these options are misaligned, the gearbox runs tough, generates extra warmth, and wears prematurely.
Robotics firms that use off-the-shelf harmonic drives from Harmonic Drive Programs or related suppliers nonetheless want customized casings as a result of the gearbox should combine with a selected motor, encoder, and joint construction.
This is without doubt one of the most regularly outsourced machined elements within the business as a result of few robotics startups have the grinding and precision boring tools wanted to complete these elements in-house.
3. Motor Mounting Plates and Flanges
The motor mount connects the servo motor to the gearbox and joint construction. It looks like a easy half, a flat plate with a bolt sample and a central bore, however the tolerances on it decide whether or not the motor shaft aligns correctly with the gearbox enter.
Misalignment between the motor and gearbox, even by a couple of hundredths of a millimeter, creates vibration that the robotic’s controller has to compensate for. In high-speed pick-and-place functions, this vibration limits cycle time as a result of the controller wants additional settling time after every transfer.
In collaborative robots that function near folks, vibration additionally impacts the accuracy of force-torque sensing on the joints.
Motor mounts are easy CNC milling jobs, normally 3-axis work in aluminum or metal. The crucial dimension is the concentricity of the pilot bore relative to the bolt sample. Good drawings name this out with GD&T place tolerances of 0.02mm or much less.
It’s a easy half to machine, however outlets that don’t take note of fixture alignment will produce elements that technically move particular person dimension checks whereas nonetheless being out of place as an meeting.
4. Finish Effector Interface Plates
The top effector interface, additionally known as the software flange, is the plate on the finish of the robotic arm the place grippers, welding torches, meting out heads, and different instruments connect. ISO 9409-1 defines a set of ordinary flange patterns for this interface, and most industrial robots observe a type of requirements.
The machining necessities are pushed by the truth that this plate is the datum for every little thing the robotic does. If the flange face isn’t perpendicular to the final axis of rotation, the software middle level shifts with each rotation, and the robotic can’t hit its programmed positions precisely.
Flatness and perpendicularity on the flange face are usually specified inside 0.01mm to 0.02mm.
These are normally turned elements completed on a CNC lathe with reside tooling for the bolt holes and dowel pin holes. The dowel pin holes are crucial characteristic as a result of they find the software relative to the flange, they usually have to be reamed to H7 tolerance or tighter.
A sloppy dowel match means the software shifts barely every time it’s reinstalled, defeating the aim of the finding characteristic.
5. Hyperlink Buildings (Arm Segments)
The hyperlink constructions are the arm segments that join one joint to the subsequent. They outline the robotic’s attain, payload capability, and stiffness. In smaller cobots, these are sometimes aluminum extrusions or forged elements which might be finish-machined.
In bigger industrial robots, they’re usually CNC-machined from aluminum billet or fabricated from welded metal after which machined to closing dimensions.
The machining on hyperlink constructions focuses on the joint mounting interfaces at every finish. These faces should be flat and parallel to one another inside tight tolerances as a result of any angular error between joints accumulates alongside the arm.
A 0.1-degree tilt at one joint can translate to a number of millimeters of positional error on the software tip, relying on the arm size.
Weight is all the time a priority with hyperlink constructions as a result of each gram within the arm reduces payload capability. This is the reason many robotics firms design hyperlinks with inner pocketing, skinny partitions, and natural shapes that take away materials with out sacrificing stiffness.
These options push the machining towards 5-axis milling with long-reach tooling, which will increase the price per half however improves the robotic’s general performance-to-weight ratio.
Device geometry decisions throughout these operations immediately have an effect on floor end and dimensional accuracy, particularly on thin-walled pockets the place chatter is a continuing threat.
6. Bearing Seats and Shaft Interfaces
Industrial robots use cross-roller bearings, angular contact bearings, or thin-section bearings at every joint, and these bearings want exactly machined seats to perform correctly.
The bearing seat is the cylindrical floor that the bearing outer ring presses into, and the shaft interface is the floor that helps the inside ring.
The tolerance necessities are set by the bearing producer. A typical cross-roller bearing for a robotic joint requires an H5 or H6 bore tolerance on the housing aspect and a j5 or k5 shaft tolerance on the inside ring aspect. In observe, this implies the machined bore must be correct to inside a couple of microns.
CNC turning or precision boring is the usual course of, adopted by grinding if the required tolerance is tighter than what the lathe can maintain.
Getting these matches unsuitable has rapid penalties. A unfastened housing match permits the outer ring to creep, producing warmth and carrying the bore. A decent shaft match can preload the bearing past its design restrict, lowering service life.
Each failure modes manifest as elevated joint friction and, finally, positioning errors that the robotic’s controller can’t calibrate out. Precision elements like these are sometimes the distinction between a robotic that holds spec over 1000’s of hours and one which drifts out of calibration inside months.
7. Encoder and Sensor Mounting Options
Correct place suggestions is what separates an industrial robotic from a easy actuator. Optical or magnetic encoders at every joint measure rotation to resolutions as high quality as 0.001 levels. However that decision is meaningless if the encoder isn’t mounted so it stays aligned with the axis of rotation.
Encoder mounts are small options, typically only a bored pocket and a set of tapped holes on the again aspect of a joint housing. However the place and concentricity of the bore that holds the encoder studying head relative to the encoder disk or ring should be managed to inside ±0.01mm.
Any eccentricity between the studying head and the disk introduces a once-per-revolution sinusoidal error within the place suggestions, which immediately degrades the robotic’s repeatability.
Drive-torque sensors, proximity sensors, and restrict switches additionally require machined mounting surfaces. These options are straightforward to miss throughout design as a result of they’re small, however they typically trigger essentially the most issues throughout meeting if the machining isn’t exact.
Why These Parts Matter for Robotics Sourcing
All seven of those elements share a typical thread. They require tolerances tighter than these for general-purpose machining however not so excessive that unique tools is required.
The candy spot for many robotics elements is ±0.01mm to ±0.025mm, which falls inside the functionality of a reliable CNC store with well-maintained tools and skilled machinists.
The actual problem for robotics firms, particularly startups and mid-size corporations scaling manufacturing, is discovering suppliers who can maintain these tolerances persistently throughout batches.
A store that hits spec on the primary 5 prototypes however drifts on a manufacturing order of 500 creates a top quality drawback that surfaces solely after the robots are already assembled. That is the place provider verification, tools audits, and structured quoting processes matter greater than the bottom per-part value.
Robotics engineering groups that make investments time in understanding the machining necessities behind their designs will make higher sourcing choices, write higher drawings, and spend much less time troubleshooting meeting and efficiency points downstream.