Machine studying tasks work greatest once they join concept to actual enterprise outcomes. In e-commerce, which means higher income, smoother operations, and happier prospects, all pushed by knowledge. By working with sensible datasets, practitioners find out how fashions flip patterns into choices that truly matter.
This text walks by means of a full machine studying workflow utilizing an Amazon gross sales dataset, from drawback framing to a submission prepared prediction file. It provides learners a transparent view of how fashions flip insights into enterprise worth, on this article.
Understanding the issue assertion
Earlier than continuing with the coding half, it’s important to look as much as the issue assertion and perceive it. The dataset consists of Amazon e-commerce transactions which present genuine on-line procuring patterns from precise on-line retail actions.
The first goal of this mission is to foretell order outcomes and analyze revenue-driving components utilizing structured transactional knowledge. The event course of requires us to create a supervised machine studying mannequin which learns from previous transaction knowledge to forecast outcomes on new check datasets.
Key Enterprise Questions Addressed
- Which components affect the ultimate order quantity?
- How do reductions, taxes, and delivery prices have an effect on income?
- Can we predict order standing or whole transaction worth precisely?
- What insights can companies extract to enhance gross sales efficiency?
In regards to the dataset
The dataset consists of 100,000 e-commerce transactions which comply with Amazon’s transaction type and embody 20 organized knowledge fields. The artificial knowledge displays genuine buyer conduct patterns along with precise enterprise operation processes.
The information set comprises details about worth modifications throughout totally different product varieties and buyer age teams and their fee choices and their order monitoring statuses. The information set comprises properties which make it appropriate for machine studying and analytical work and dashboard growth.
| Part | Discipline Title |
|---|---|
| Order Particulars | OrderID |
| OrderDate | |
| OrderStatus | |
| SellerID | |
| Buyer Info | CustomerID |
| CustomerName | |
| Metropolis | |
| State | |
| Nation | |
| Product Info | ProductID |
| ProductName | |
| Class | |
| Model | |
| Amount | |
| Pricing & Income Metrics | UnitPrice |
| Low cost | |
| Tax | |
| ShippingCost | |
| TotalAmount | |
| Cost Particulars | PaymentMethod |
Load important Python Libraries
To work on the mannequin growth course of first it requires important Python library imports to deal with knowledge work. The mixture of Pandas and NumPy will allow us to carry out each knowledge dealing with duties and mathematical calculations. Our visualization wants can be fulfilled by means of using Matplotlib and Seaborn. Scikit-learn supplies features for preprocessing and ML algorithms. Right here is the everyday set of imports:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, accuracy_scoreThe libraries allow us to carry out 4 important actions which embody loading CSV knowledge, executing knowledge cleaning and transformation processes, utilizing charts for pattern evaluation, and constructing a classification mannequin.
Load the datasets
We are going to import knowledge right into a Pandas dataFrame after we full the environment setup. The uncooked CSV file undergoes transformation by means of this step into an analyzable and programmatically manipulatable format.
df = pd.read_csv("Amazon.csv")
print("Form:", df.form)Form: (100000, 20)
We have to verify the info construction after loading as a result of we want affirmation that it was imported accurately. The dataset dimensions are checked whereas we seek for any preliminary issues that have an effect on knowledge high quality.
print("nMissing values:n", df.isna().sum())
df.head()Lacking values:OrderID 0
OrderDate 0
CustomerID 0
CustomerName 0
ProductID 0
ProductName 0
Class 0
Model 0
Amount 0
UnitPrice 0
Low cost 0
Tax 0
ShippingCost 0
TotalAmount 0
PaymentMethod 0
OrderStatus 0
Metropolis 0
State 0
Nation 0
SellerID 0dtype: int64
| OrderID | OrderDate | CustomerID | CustomerName | ProductID | ProductName | Class | Model | Amount | UnitPrice | Low cost | Tax | ShippingCost | TotalAmount | PaymentMethod | OrderStatus | Metropolis | State | Nation | SellerID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORD0000001 | 2023-01-31 | CUST001504 | Vihaan Sharma | P00014 | Drone Mini | Books | BrightLux | 3 | 106.59 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 319.86 | Debit Card | Delivered | Washington | DC | India | SELL01967 |
| ORD0000002 | 2023-12-30 | CUST000178 | Pooja Kumar | P00040 | Microphone | House & Kitchen | UrbanStyle | 1 | 251.37 | 0.05 | 19.10 | 1.74 | 259.64 | Amazon Pay | Delivered | Fort Price | TX | United States | SELL01298 |
| ORD0000003 | 2022-05-10 | CUST047516 | Sneha Singh | P00044 | Energy Financial institution 20000mAh | Clothes | UrbanStyle | 3 | 35.03 | 0.10 | 7.57 | 5.91 | 108.06 | Debit Card | Delivered | Austin | TX | United States | SELL00908 |
| ORD0000004 | 2023-07-18 | CUST030059 | Vihaan Reddy | P00041 | Webcam Full HD | House & Kitchen | Zenith | 5 | 33.58 | 0.15 | 11.42 | 5.53 | 159.66 | Money on Supply | Delivered | Charlotte | NC | India | SELL01164 |
Information Preprocessing
1. Decomposing Date Options
Fashions can not do math on a string like “2023-01-31”. The 2 parts “Month: 1” and “12 months: 2023” create important numerical attributes which may detect seasonal patterns together with vacation gross sales.
df["OrderDate"] = pd.to_datetime(df["OrderDate"], errors="coerce")
df["OrderYear"] = df["OrderDate"].dt.yr
df["OrderMonth"] = df["OrderDate"].dt.month
df["OrderDay"] = df["OrderDate"].dt.dayNow we have efficiently extracted three new options: OrderYear, OrderMonth, and OrderDay. The mannequin learns patterns which present “December brings larger gross sales” and “weekend days produce elevated gross sales”.
2. Dropping Irrelevant Options
The mannequin requires solely particular columns. The distinctive ID identifiers (OrderID, CustomerID) don’t present predictive data which ends up in mannequin coaching knowledge memorization by means of overfitting. We additionally dropped OrderDate since we simply extracted its helpful elements.
cols_to_drop = [
"OrderID",
"CustomerID",
"CustomerName",
"ProductID",
"ProductName",
"SellerID",
"OrderDate", # already decomposed
]
df = df.drop(columns=cols_to_drop)The dataframe now comprises solely important parts which create predictive worth. The mannequin now detects widespread patterns by means of product class and tax charges whereas we take away particular buyer ID data which may create “leakage” and noise.
3. Dealing with Lacking Values
The preliminary verify confirmed no lacking values however we want our methods to deal with real-world circumstances. The mannequin will crash if upcoming knowledge comprises lacking data. We implement a security web by filling gaps with the median (for numbers) or “Unknown” (for textual content).
print("nMissing values after transformations:n", df.isna().sum())
# If any lacking values in numeric columns, fill with median
numeric_cols = df.select_dtypes(embody=["int64", "float64"]).columns.tolist()
for col in numeric_cols:
if df[col].isna().sum() > 0:
df[col] = df[col].fillna(df[col].median())Class 0
Model 0
Amount 0
UnitPrice 0
Low cost 0
Tax 0
ShippingCost 0
TotalAmount 0
PaymentMethod 0
OrderStatus 0
Metropolis 0
State 0
Nation 0
OrderYear 0
OrderMonth 0
OrderDay 0
dtype: int64
# For categorical columns, fill with "Unknown"
categorical_cols = df.select_dtypes(embody=["object"]).columns.tolist()
for col in categorical_cols:
df[col] = df[col].fillna("Unknown")
print("nFinal dtypes after cleansing:n")Class object
Model object
Amount int64
UnitPrice float64
Low cost float64
Tax float64
ShippingCost float64
TotalAmount float64
PaymentMethod object
OrderStatus object
Metropolis object
State object
Nation object
OrderYear int32
OrderMonth int32
OrderDay int32
dtype: object
The pipeline is now bulletproof. The ultimate dtypes verify confirms that our knowledge is absolutely prepped: all categorical variables are objects (prepared for encoding) and all numerical variables are int32 or float64 (prepared for scaling).
Exploratory knowledge evaluation (EDA)
The Information Evaluation course of begins with our preliminary examination of knowledge which we deal with as an interview course of to be taught in regards to the knowledge’s traits. Our investigation contains three important parts which we use to establish patterns and outliers and look at distributional traits.
Statistical Abstract: We have to perceive the mathematical properties of our numerical columns. Are the costs cheap? Are there any destructive values that exist in prohibited areas?
# 2. Fundamental Information Understanding / EDA (light-weight)
print("nDescriptive stats (numeric):n")
df.describe()The descriptive statistics desk supplies crucial context:
- Amount: The measurement goes from 1 to five with three as its common worth. Shoppers who store at retail shops have a tendency to point out this conduct which companies use for his or her B2B purchases.
- UnitPrice: The value ranges between 5.00 and 599.99 which reveals that there exists a number of product tiers.
The goal variable TotalAmount reveals broad variance as a result of its commonplace deviation approaches 724 which implies our mannequin should keep its capability to course of transactions starting from small purchases to most purchases of 3534.98.
Categorical Evaluation
We have to know the cardinality (variety of distinctive values) of our categorical options. The mannequin experiences bloat and overfitting points as a result of excessive cardinality happens when there are millions of distinctive cities within the dataset.
print("nUnique values in some categorical columns:")
for col in ["Category", "Brand", "PaymentMethod", "OrderStatus", "Country"]:
print(f"{col}: {df[col].nunique()} distinctive")Distinctive values in some categorical columns:Class: 6 distinctive
Model: 10 distinctive
PaymentMethod: 6 distinctive
OrderStatus: 5 distinctive
Nation: 5 distinctive
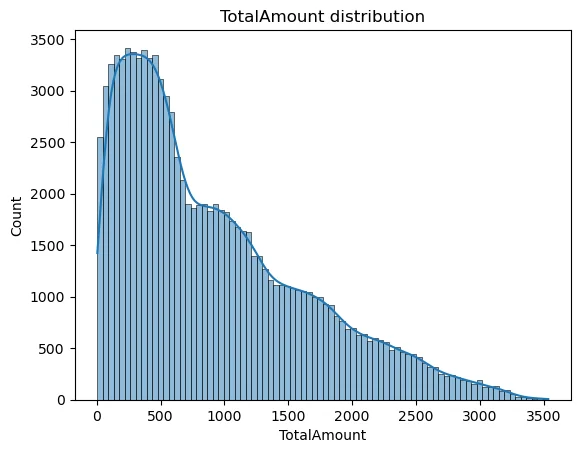
Visualizing the Goal Distribution
The histogram reveals the frequency of various transaction quantities. A easy curve (KDE) permits us to see the density. With the curve being barely proper skewed subsequently tree-based fashions like Random Forest deal with very nicely.
sns.histplot(df["TotalAmount"], kde=True)
plt.title("TotalAmount distribution")
plt.present()The TotalAmount visualization permits us to find out whether or not the info displays any skewed distribution. The information requires a Log Transformation when it reveals excessive skewness with only some high-priced merchandise and quite a few low-cost gadgets.
Function Engineering
Function engineering develops new variables by means of the method of remodeling present variables to spice up mannequin efficiency. In Supervised Studying, we should explicitly inform the mannequin what to foretell (y) and what knowledge to make use of to make that prediction (X).
target_column = "TotalAmount"
X = df.drop(columns=[target_column])
y = df[target_column]
numeric_features = X.select_dtypes(embody=["int64", "float64"]).columns.tolist()
categorical_features = X.select_dtypes(embody=["object"]).columns.tolist()
print("nNumeric options:", numeric_features)
print("Categorical options:", categorical_features)Splitting the prepare and check knowledge
The mannequin analysis course of requires separate knowledge as a result of coaching knowledge can’t be used for evaluation, which parallels the observe of offering college students with examination solutions earlier than the check. The information distribution consists of two elements: Coaching Set which serves academic functions and Check Set which verifies outcomes.
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
print("nTrain form:", X_train.form, "Check form:", X_test.form)Right here now we have used the 80-20 % rule, which implies randomly out of all the info now we have 80% can be used because the prepare knowledge and the remaining 20% can be used to check it because the check knowledge set.
Construct Machine Studying Mannequin
Creating the ML pipeline would concerned the next processes:
1. Creating Preprocessing Pipelines
The uncooked numbers of every measurement scale otherwise as a result of they embody measurements that vary from 1 to five for Amount and from 5 to 500 for Value. The fashions obtain sooner convergence when researchers implement knowledge scaling methods. One-Sizzling Encoding supplies the mandatory technique to remodel categorical textual content into numerical format. The ColumnTransformer system permits us to use totally different transformation strategies for each column sort in our dataset.
numeric_transformer = Pipeline(
steps=[
("scaler", StandardScaler())
]
)
categorical_transformer = Pipeline(
steps=[
("onehot", OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown="ignore"))
]
)
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(
transformers=[
("num", numeric_transformer, numeric_features),
("cat", categorical_transformer, categorical_features),
]
)2. Defining the Random Forest Mannequin
Now we have chosen the Random Forest Regressor for this mission. The ensemble technique constructs a number of choice timber which it makes use of to compute forecast outcomes by means of prediction averaging. The system demonstrates robust robustness towards overfitting issues whereas it excels at managing non-linear connections between variables.
mannequin = RandomForestRegressor(
n_estimators=200,
max_depth=None,
random_state=42,
n_jobs=-1
)
# Full pipeline
regressor = Pipeline(
steps=[
("preprocessor", preprocessor),
("model", model),
]
)We created the mannequin with n_estimators=200 to construct 200 choice timber and n_jobs=-1 to allow all CPU cores for speedier mannequin growth. One of the best observe for this implementation requires customers to create a single Pipeline object which mixes the preprocessor and mannequin to deal with their whole operational course of as one unit.
3. Coaching the Mannequin
This stage represents the first studying course of. The pipeline processes coaching knowledge by means of transformation steps earlier than it makes use of the Random Forest mannequin on the transformed knowledge.
regressor.match(X_train, y_train)
print("nModel coaching full.")The mannequin now understands how totally different enter variables (Class Value Tax and many others.) relate to the output variable (Complete Quantity).
Make predictions on the check dataset
Now we check the mannequin on the check knowledge (i.e, 20,000 “unseen” data). The mannequin efficiency evaluation makes use of statistical metrics to match its predicted outcomes (y_pred) with the precise outcomes (y_test).
y_pred = regressor.predict(X_test)
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
rmse = np.sqrt(mse)
r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("nTest metrics:")
print("MAE :", mae)
print("MSE :", mse)
print("RMSE:", rmse)
print("R2 :", r2)Check metrics:MAE : 3.886121525000014
MSE : 41.06268576375389
RMSE: 6.408017303640331
R2 : 0.99992116450905
This signifies:
- The Imply Absolute Error (MAE) worth stands at roughly 3.88. Our prediction reveals a mean error of $3.88.
- The R2 Rating worth stands at roughly 0.9999. That is close to excellent. The impartial variables (Value, Tax, Transport) nearly totally account for the Complete Quantity in response to this end result. The Complete components in artificial monetary knowledge follows the equation Complete = Value * Qty + Tax + Transport – Low cost.
Put together submission file
The system requires contributors to current their predictions in response to predetermined output specs which should not be altered.
submission = pd.DataFrame({
"OrderID": df.loc[X_test.index, "OrderID"],
"PredictedTotalAmount": y_pred
})
submission.to_csv("submission.csv", index=False)The analysis system accepts this file for direct submission whereas stakeholders may also obtain it.
Conclusion
This machine studying mission demonstrates its full course of by means of demonstration of uncooked e-commerce transaction knowledge transformation into helpful predictive outcomes. The structured workflow technique allows you to handle precise datasets with full assurance and understanding of the method. The success of the mission depends upon the 5 steps which embody preprocessing and EDA and have engineering and modeling.
The mission helps in creating your machine studying capabilities whereas coaching you to deal with actual work conditions. The pipeline wants further optimization work earlier than it could operate as a advice system with superior fashions or deep studying methods.
Ceaselessly Requested Questions
A. It goals to foretell the full order quantity utilizing transactional and pricing knowledge.
A. It captures advanced patterns and reduces overfitting by combining many choice timber.
A. It contains OrderID and the mannequin’s predicted whole quantity for every order.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.