Cognibotics is contributing its movement software program to the Vinnova-funded CAISA (Collaborative Synthetic Clever Surgical Assistant) challenge because it enters the demonstrator part.
In CAISA, Cognibotics supplies the movement layer between AI-based notion and path planning modules.
In distinction to utilizing the usual robotic controller, Cognibotics answer allows the robotic to be commanded in numerous methods as AI and planning modules require – supporting constant, maintainable, but dynamic instrument dealing with in a non-clinical paediatric coronary heart surgical procedure analysis testbed.
From surgical knowledge to movement demonstrator
CAISA is a collaboration between Area Skåne (Paediatric Coronary heart Centre at Skåne College Hospital), Lund College, Cognibotics and Cobotic. The challenge is funded by Vinnova with SEK 10 million (roughly $1.1 million) and runs from September 2024 to August 2027.
Within the preliminary part, a number of key constructing blocks have been put in place:
1. Giant-scale surgical video dataset for mannequin improvement
The Paediatric Coronary heart Centre has collected a surgical video database of greater than 3,000 hours. This knowledge is used to coach AI fashions that recognise and estimate the pose of devices, arms, and cardiac anatomy.
2. Full-scale testbed for validation
On the hospital campus, an innovation and testbed facility of roughly 350 m² features a full working room atmosphere, with the likelihood to work with donated our bodies for analysis. This supplies a managed setting for evaluating robotics and security features earlier than any scientific deployment is taken into account.
3. Clear requirement for a demonstrator
Within the Vinnova challenge description, the creation, testing, and validation of a demonstrator on this devoted check atmosphere is an specific aim. The challenge is now coming into this demonstrator part.
Cognibotics: Movement-control layer for an AI-guided assistant
Inside CAISA, Cognibotics focuses on the movement layer that connects a number of “methods of commanding” the robotic. Cognibotics supplies a unified movement interface the place notion, planning, and utility logic can drive movement in a constant, predictable means within the testbed atmosphere.
By bringing expertise from high-precision industrial robots into the surgical analysis context, Cognibotics contributes strategies for:
- model-based movement management with consideration to atmosphere constraints;
- fine-grained positioning in a confined workspace across the affected person; and
- movement behaviours that may assist protected, repeatable interactions between human surgeon, devices and robotic.
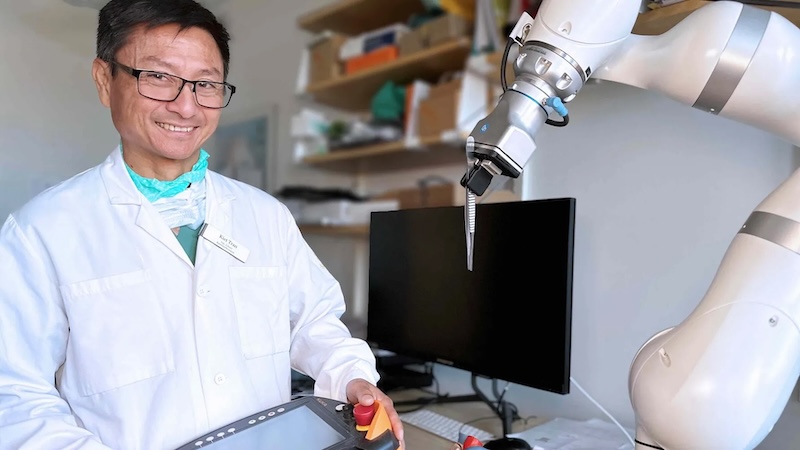
Phan-Kiet Tran, senior marketing consultant in paediatric coronary heart surgical procedure at Skåne College Hospital and affiliate professor at Lund College, says: “In CAISA we’re combining world-class paediatric coronary heart surgical procedure, superior AI and Cognibotics’ experience in movement management.
“The robotic should not solely ‘perceive’ the state of affairs, it additionally has to maneuver devices in a means that feels pure, protected and repeatable for the entire workforce. Cognibotics supplies that industrial-grade movement layer, which is crucial if an AI assistant is for use in actual working rooms.”
From business to future surgical functions
Cognibotics’ movement expertise is already utilized in demanding industrial settings resembling high-speed warehouse robots and precision machining. CAISA extends that experience into the medical analysis area, exploring how an analogous motion-control basis can assist future AI-guided surgical assistants.
The demonstrator developed in CAISA is strictly a analysis platform in a non-clinical atmosphere. Nonetheless, the challenge goals to construct the technical and scientific understanding wanted for future methods the place AI, surgeons and robots work collectively extra safely and effectively.