As the development sector grapples with cussed labor shortages, rising prices, and mounting stress to ship housing at scale, a brand new class of automation firms is rising that guarantees to reshape how properties are constructed.
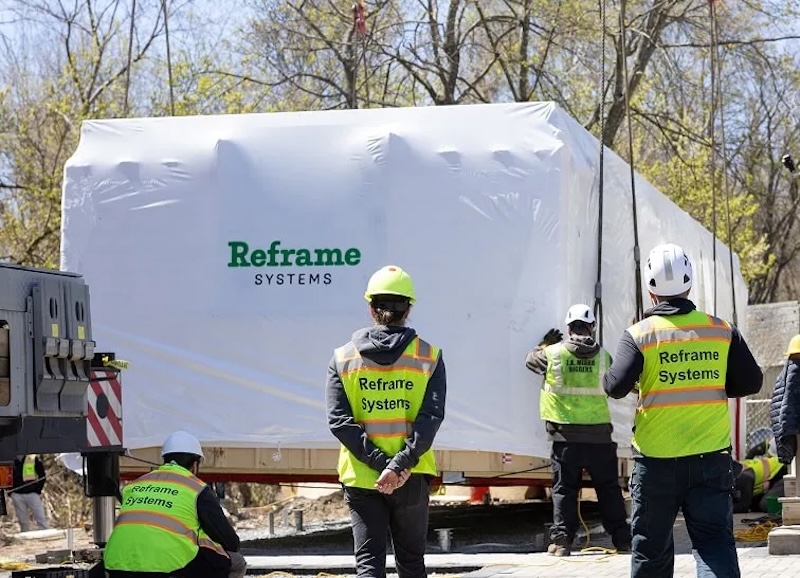
Probably the most intriguing amongst them is Reframe Systems, a expertise firm that blends industrial robotics, synthetic intelligence, and superior manufacturing to automate massive chunks of the development course of which have lengthy resisted mechanization.
Based on the conviction that real-world productiveness beneficial properties require greater than remoted bricklaying robots or easy materials movers, Reframe describes its strategy as “bodily AI” for building – making use of robotics and automation inside managed manufacturing unit environments to ship repeatable, high-quality constructing elements at scale.
Quite than chasing headlines with site-borne robots, the corporate focuses on the manufacturing unit flooring the place panel fabrication, framing, chopping, fastening, and materials dealing with could be accomplished with precision and consistency below machine management.
On the helm is Vikas Enti, CEO and co-founder of Reframe Systems. Enti is a veteran of Amazon Robotics who helped oversee the deployment of greater than half 1,000,000 robots in high-volume logistics environments.

Enti’s expertise in scaling automation for one of many world’s most demanding manufacturing networks now informs Reframe’s mission: to unlock important parts of housing manufacturing by means of built-in robotics, whereas nonetheless preserving expert builders on the coronary heart of the craft-driven ending work that defines high quality properties.
On this e-mail Q&A, Enti walks us by means of how Reframe’s automation programs work as we speak, the place the business nonetheless lags, and what the broader market may appear like if building embraced automation not simply as a set of instruments, however as a elementary manufacturing mannequin – one able to boosting capability, bettering security, and reducing value and carbon footprints in one of many world’s most difficult sectors.
Interview with Vikas Enti, CEO and co-founder, Reframe Programs

Robotics & Automation Information: Reframe describes its course of as “bodily AI” for building. On the sensible degree, what robotics programs are you deploying as we speak on the manufacturing unit flooring, and which phases of homebuilding are at present automated finish to finish?
Vikas Enti: We’re growing a robotics and imaginative and prescient platform to unlock automation of roughly 60 % to 80 % of labor content material.
At present, our main focus for automation is in panel manufacturing.
Contained in the manufacturing community, robots tackle the repetitive and bodily demanding duties concerned in framing and assembling wall and ceiling panels – measuring, chopping, fastening, dealing with supplies and extra that may historically be lifted and aligned manually.
Past that, people lead module meeting, MEP, finishes, and all on-site set up as these require adaptability and discipline experience. Our objective is to proceed increasing automation inside the manufacturing unit over time, whereas preserving expert labor central to the general course of.
R&AN: Development automation has historically centered on remoted duties like bricklaying, welding, or materials transport. What components of your course of are automated that aren’t usually automated elsewhere within the building sector?
VE: Most building robotics focuses on single duties – like bricklaying, welding, or transferring supplies. Our mannequin automates the repetitive steps required to fabricate panels that meet native codes and power requirements. As an alternative of automating one motion, we automate a key part of the manufacturing sequence inside a manufacturing community.
As a result of our manufacturing networks function indoors and in managed situations, we will automate work that may usually occur on an open jobsite – resembling framing, fastening, and dealing with heavy supplies – and do it with consistency no matter climate or web site situations.
R&AN: You come from Amazon Robotics, the place you oversaw implementation of greater than 500,000 robots. How a lot of that have interprets on to building, and the place did you discover the most important variations in making use of high-scale automation to a sector that has traditionally resisted it?
VE: Plenty of the basics translate straight: programs engineering, workflow automation, security, and integrating robots that interface with folks to mass-customize orders.
The most important distinction is clearly the quantity of labor content material in constructing a house vs assembling an ecommerce order.
At Reframe, we took the components of Amazon’s playbook that work (standardized inputs and work, automation of repetitive duties, augmenting people with superior interfaces) and tailored them to our personal distributed manufacturing community constructed for the real-world constraints of housing.
R&AN: What share of Reframe’s manufacturing workflow is at present automated, and what number do you consider is realistically automatable inside the subsequent 3-5 years?
VE: We’re at present automating about 20 % of the duties with framing of partitions and ceilings.
Over time, we’re aiming to automate 60-80 % of manufacturing unit duties, together with ending duties (portray, drywall), insulation, element set up (home windows, cupboards) and inspections
R&AN: You’ve emphasised that your robots take over repetitive and bodily demanding duties somewhat than change expert labour. Are you able to give examples of duties which were “robotised” at Reframe, and the way that has modified the position of the builder or craftsperson?
VE: Panel fabrication duties like chopping, fastening, lifting, and aligning framing elements at the moment are dealt with by robotics contained in the manufacturing community. These duties are bodily taxing and repetitive, making them good candidates for automation.
Builders now give attention to higher-skill work – putting in home windows and doorways, performing MEP, finishing finishes, and dealing with the small print that outline high quality. Automation reduces bodily pressure whereas giving staff extra time for the craft-driven components of building.
R&AN: Reframe says it may well construct properties 2.5x sooner, at 35 % decrease value, and with 10x fewer emissions. How a lot of those beneficial properties are straight attributable to robotics and automation, versus design, supplies, or course of engineering?
VE: The beneficial properties come from the whole system working collectively. Automation improves throughput and consistency within the manufacturing unit, however equally vital are:
- Manufacturing networks positioned near tasks, decreasing delays and transportation prices
- Off-site manufacturing, which permits parallel web site prep and manufacturing unit work
- Standardized constructing programs that cut back rework and uncertainty
- All-electric, solar-ready, fire-resilient designs that cut back operational and embodied carbon
Automation is a key enabler, however the velocity, value, and carbon enhancements come from combining robotics with a brand new manufacturing mannequin and a climate-resilient constructing platform.
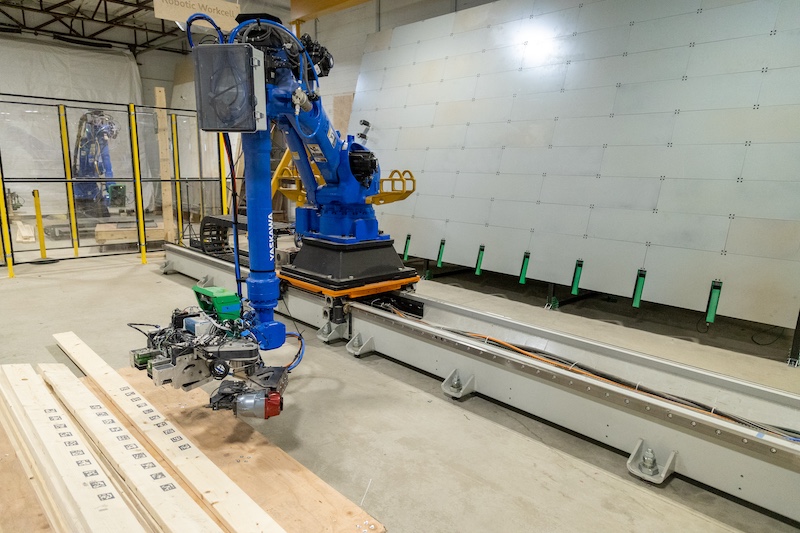
R&AN: If the broader building business adopted the extent of automation you’re growing, the place do you see the most important impression: labour shortages, security, value discount, high quality management, carbon discount – or one thing else fully?
VE: Essentially the most fast impression can be increasing total manufacturing capability – addressing the labor scarcity by decreasing the quantity of repetitive, bodily demanding work and letting builders give attention to higher-skill duties.
Past that, factory-built elements enhance consistency, security, and high quality whereas decreasing building waste and carbon footprint. Automating the proper segments of the workflow would assist produce properties extra predictably and on the scale wanted to handle each housing and local weather challenges.
With a 4.7 million residence scarcity, the US can’t afford incremental beneficial properties. If the business adopted the extent of automation we’re constructing, we may develop capability the place it issues most.
That’s on the core of Reframe’s mission: use automation to multiply human functionality so communities can get high-quality, climate-ready housing on a timeline that matches the dimensions of the disaster.