How will you guarantee your machine studying fashions get the high-quality information they should thrive? In at this time’s machine studying panorama, dealing with information effectively is as necessary as constructing sturdy fashions. Feeding high-quality, well-structured information into your fashions can considerably influence efficiency and coaching pace. The TensorFlow Dataset API simplifies this course of by providing set of instruments to construct, handle, and optimize information pipelines. On this information, we’ll go step-by-step from configuring your growth atmosphere utilizing Vertex AI Workbench to loading information from numerous sources and incorporating these pipelines into your mannequin coaching course of.
Studying Targets
- Construct datasets from in-memory arrays in addition to exterior information sources reminiscent of CSV and TFRecord recordsdata.
- Make the most of operations reminiscent of mapping, shuffling, batching, caching, and prefetching to streamline information processing.
- Seamlessly incorporate your datasets into TensorFlow’s mannequin coaching routines for environment friendly mannequin growth.
- Be taught to launch a Vertex AI Workbench occasion, arrange a Jupyter Pocket book, and begin working.
- Improve your machine studying fashions by making use of information augmentation strategies immediately in your information pipelines.
This text was revealed as part of the Knowledge Science Blogathon.
What’s TensorFlow?
TensorFlow is an open-source platform developed by Google for machine studying and deep studying analysis. It supplies an in depth ecosystem of instruments and libraries, permitting researchers to push the boundaries of what’s doable in machine studying and enabling builders to construct and deploy clever functions with ease. TensorFlow helps each high-level APIs (like Keras) and low-level operations, making it accessible for rookies whereas remaining highly effective for superior customers.
What’s Vertex AI Workbench?
Vertex AI Workbench is a managed growth atmosphere in Google Cloud that’s designed that can assist you construct and prepare machine studying fashions. It supplies a completely managed Jupyter Pocket book expertise together with preinstalled machine studying libraries, together with TensorFlow and PyTorch. With Vertex AI Workbench, you’ll be able to seamlessly combine your native growth with cloud computing sources, making it simpler to work on large-scale initiatives with out worrying about infrastructure setup.
On this information, not solely will you learn to work with TensorFlow’s Dataset API, however additionally, you will see learn how to arrange your atmosphere utilizing Vertex AI Workbench. We are going to cowl every thing from launching a brand new occasion, making a Jupyter Pocket book, and loading the datasets.
Understanding the TensorFlow Dataset API
The TensorFlow Dataset API is a set of instruments designed to simplify the method of constructing information enter pipelines. In any machine studying process, your mannequin’s efficiency relies upon not simply on the algorithm itself but additionally on the standard and circulate of the info being fed into it. The Dataset API lets you carry out duties like loading information, preprocessing it, and remodeling it on the go.
What makes this API so highly effective is its potential to chain a number of operations in a single, easy-to-understand sequence. You possibly can load information from numerous sources, apply essential transformations (reminiscent of scaling or normalization), and even shuffle the info to forestall the mannequin from overfitting. This strategy not solely makes your code cleaner and simpler to take care of, nevertheless it additionally optimizes efficiency by leveraging strategies like caching and prefetching.
Setting Up Your Surroundings with Vertex AI Workbench
Earlier than you begin working with the TensorFlow Dataset API, you want a strong atmosphere. Vertex AI Workbench is a wonderful alternative for this objective as a result of it affords a completely managed, cloud-based growth atmosphere that comes with all of the instruments you want pre-installed.
Launch Vertex AI Workbench Occasion
- Begin by logging into your Google Cloud account. From the Navigation menu, search and choose Vertex AI.
- Click on on the “Allow All Really useful APIs” button. This ensures that your undertaking has entry to all the required API providers.
- Within the navigation menu, click on on Workbench. Be sure to are within the Situations view.
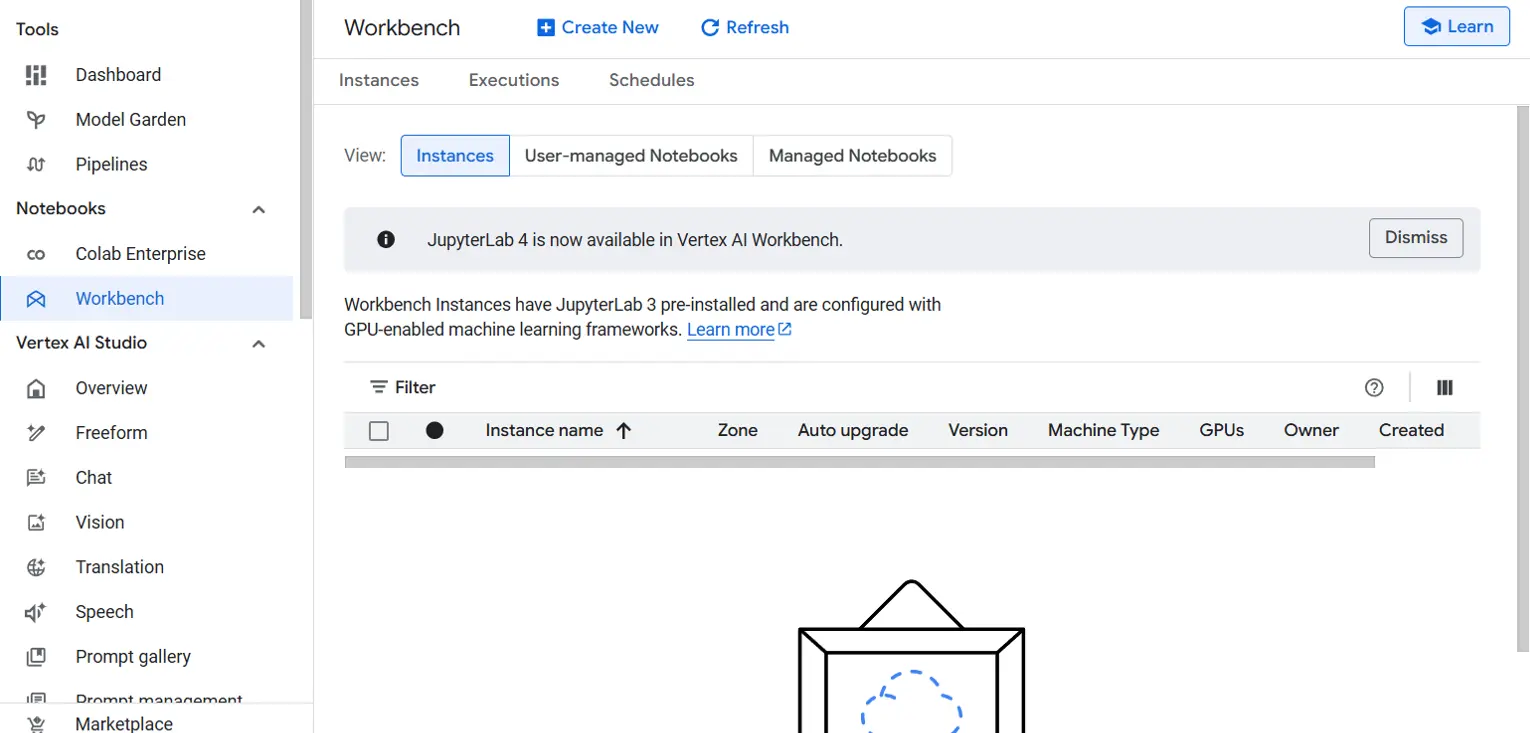
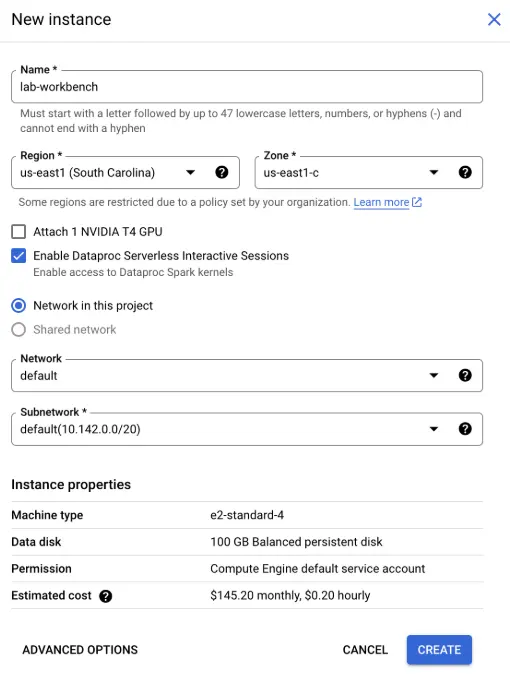
- Click on on Create New to launch a brand new Workbench occasion. You may be prompted to configure the occasion:
- Identify: Give your occasion a significant identify, reminiscent of lab-workbench.
- Area and Zone: Choose the suitable area and zone the place you need your occasion to be situated.
- Superior Choices: If wanted, customise the occasion settings by choosing choices like machine kind or disk measurement.
- After configuration, click on Create. It would take a couple of minutes in your occasion to be arrange. As soon as it’s prepared, you will note a inexperienced checkmark subsequent to its identify.
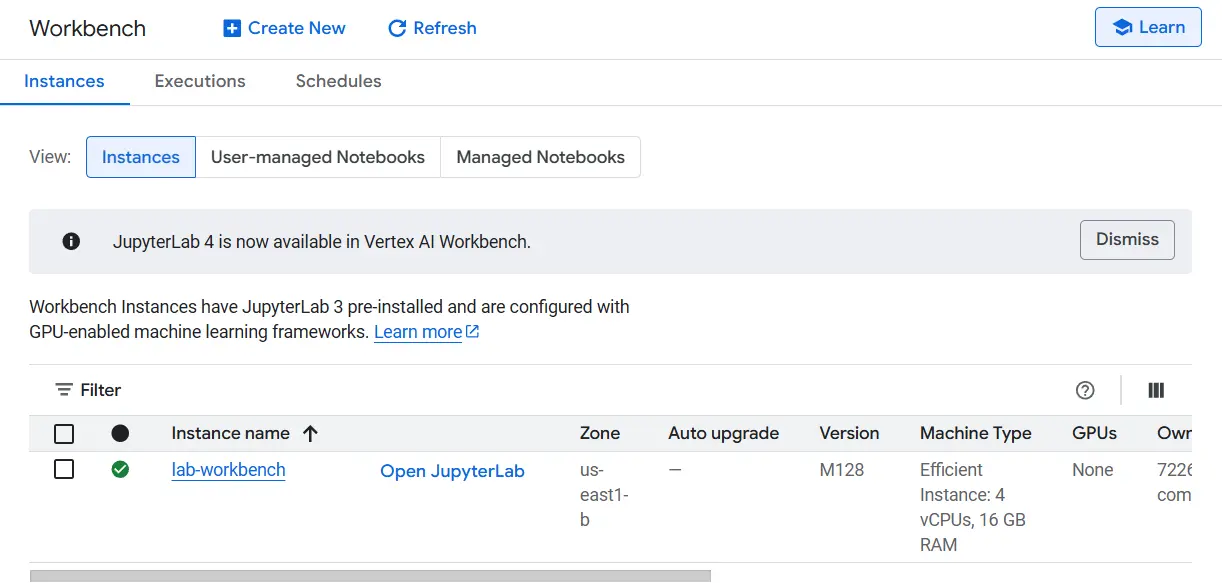
- Click on Open JupyterLab subsequent to your occasion’s identify. This may open the Jupyter Lab interface in a brand new tab in your browser.
Making a Jupyter Pocket book
After you have your JupyterLab interface open, you can begin a brand new Python Pocket book by clicking on the Python 3 icon. It’s a good suggestion to rename the pocket book to one thing descriptive. To do that, right-click on the file identify (which could initially be Untitled.ipynb) and choose Rename Pocket book. Select a reputation that displays the undertaking, reminiscent of “new_project”. Additionally change the kernel from python 3 to TensorFlow 2-11 (Native).
Manipulate information with tf.information
First add the taxi-train.csv and taxi-valid.csv dataset into the pocket book.
Importing the Required Libraries
First, we have to import TensorFlow and NumPy, after which set the TensorFlow logging stage to a minimal setting. This reduces log verbosity throughout execution.
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
print("TensorFlow model:", tf.model.VERSION)
# Set minimal TF logging stage.
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'Making a Dataset from Reminiscence
As soon as your atmosphere is about up, you can begin working with information. The best strategy to start is by making a dataset from reminiscence. This implies changing information saved in your pc’s reminiscence (like lists or NumPy arrays) right into a format that TensorFlow can course of.
Think about you have got a small set of numbers that you just need to use for a fundamental experiment. The TensorFlow Dataset API lets you shortly convert these numbers right into a dataset that may be manipulated additional. This course of is easy and will be prolonged to extra complicated information buildings.
For instance, you would possibly begin with a easy NumPy array that accommodates a number of numbers. Utilizing the Dataset API, you’ll be able to create a dataset from this array. The dataset can then be iterated over, and you may apply numerous transformations reminiscent of mapping a perform to every aspect.
Creating the Artificial Dataset
We first create an artificial dataset. On this instance, we generate our function vector X and a corresponding label vector Y utilizing the linear equation y=2x+10.
N_POINTS = 10
X = tf.fixed(vary(N_POINTS), dtype=tf.float32)
Y = 2 * X + 10 Subsequent, we outline a perform that accepts our function and label arrays, together with the variety of coaching passes (epochs) and the specified batch measurement. This perform constructs a TensorFlow Dataset by slicing the tensors, repeating them for the required variety of epochs, and batching them (dropping any remaining examples to maintain batch sizes constant).
def make_synthetic_dataset(X, Y, epochs, batch_size):
# Create the dataset from tensor slices
ds = tf.information.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X, Y))
# Repeat the dataset and batch it (drop the rest for consistency)
ds = ds.repeat(epochs).batch(batch_size, drop_remainder=True)
return ds Let’s take a look at our perform by iterating twice over our dataset in batches of three datapoints:
BATCH_SIZE = 3
EPOCHS = 2
dataset = make_synthetic_dataset(X, Y, epochs=EPOCHS, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
print("Artificial dataset batches:")
for i, (x_batch, y_batch) in enumerate(dataset):
print(f"Batch {i}: x: {x_batch.numpy()} y: {y_batch.numpy()}")
assert len(x_batch) == BATCH_SIZE
assert len(y_batch) == BATCH_SIZE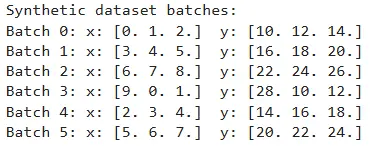
Loss Perform and Gradient Computation
Subsequent, we outline the imply squared error (MSE) loss perform and a helper perform to compute gradients. These features stay just like our earlier implementation.
def loss_mse(X, Y, w0, w1):
Y_pred = w0 * X + w1
error = (Y_pred - Y) ** 2
return tf.reduce_mean(error)
def compute_gradients(X, Y, w0, w1):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
current_loss = loss_mse(X, Y, w0, w1)
return tape.gradient(current_loss, [w0, w1]), current_lossCoaching loop
Now, we replace our coaching loop in order that it iterates over the tf.information.Dataset created by our perform. On this instance, we prepare the mannequin over 250 epochs utilizing a batch measurement of two.
First, initialize the mannequin parameters as TensorFlow variables:
# Initialize mannequin parameters
w0 = tf.Variable(0.0)
w1 = tf.Variable(0.0)
EPOCHS_TRAIN = 250
BATCH_SIZE_TRAIN = 2
LEARNING_RATE = 0.02
# Create the coaching dataset (artificial)
train_dataset = make_synthetic_dataset(X, Y, epochs=EPOCHS_TRAIN, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE_TRAIN)
Then, we run the coaching loop utilizing stochastic gradient descent. The loop updates the mannequin parameters with every batch, and we print the coaching standing each 100 steps.
# Coaching loop
print("nStarting coaching loop for artificial linear regression:")
MSG = "Step {step} - loss: {loss:.6f}, w0: {w0:.6f}, w1: {w1:.6f}"
for step, (X_batch, Y_batch) in enumerate(train_dataset):
grads, loss_val = compute_gradients(X_batch, Y_batch, w0, w1)
# Replace the parameters utilizing gradient descent
w0.assign_sub(LEARNING_RATE * grads[0])
w1.assign_sub(LEARNING_RATE * grads[1])
if step % 100 == 0:
print(MSG.format(step=step, loss=loss_val.numpy(), w0=w0.numpy(), w1=w1.numpy()))
# Remaining assertions (tolerance based mostly)
assert loss_val < 1e-6
assert abs(w0.numpy() - 2) < 1e-3
assert abs(w1.numpy() - 10) < 1e-3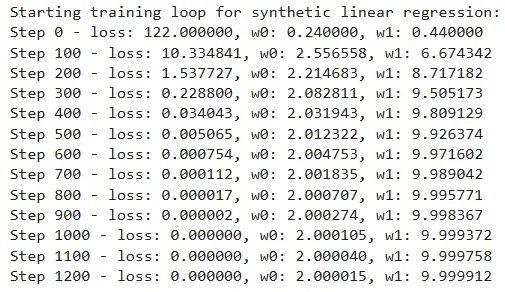
Loading Knowledge from Disk
In sensible functions, information is usually saved on disk somewhat than in reminiscence. Loading information from disk with these strategies ensures that you could deal with giant datasets effectively and put together them for mannequin coaching. Two frequent codecs for storing information are CSV and TFRecord.
Loading a CSV File
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) recordsdata are extensively used for storing tabular information. The TensorFlow Dataset API affords a handy strategy to learn CSV recordsdata. The method entails parsing every line of the file to transform textual content into numeric information, batching the outcomes, and making use of any extra transformations.
Beneath, we outline the column names and default values for our CSV file:
CSV_COLUMNS = [
'fare_amount',
'pickup_datetime',
'pickup_longitude',
'pickup_latitude',
'dropoff_longitude',
'dropoff_latitude',
'passenger_count',
'key'
]
LABEL_COLUMN = 'fare_amount'
DEFAULTS = [[0.0], ['na'], [0.0], [0.0], [0.0], [0.0], [0.0], ['na']]Subsequent, we wrap the CSV dataset creation right into a perform that reads the recordsdata based mostly on a file sample and a specified batch measurement:
def make_csv_dataset(sample, batch_size):
# Create dataset from CSV recordsdata with specified column names and defaults.
ds = tf.information.experimental.make_csv_dataset(
file_pattern=sample,
batch_size=batch_size,
column_names=CSV_COLUMNS,
column_defaults=DEFAULTS,
header=True
)
return ds
# For demonstration, assume the CSV recordsdata are situated in '../toy_data/'.
temp_ds = make_csv_dataset('taxi-train.csv', batch_size=2)
print("nSample CSV dataset (prefetched):")
print(temp_ds)
To enhance readability, let’s iterate over the primary two parts of this dataset and convert them into customary Python dictionaries:
for information in temp_ds.take(2):
print({ok: v.numpy() for ok, v in information.objects()})
print("n")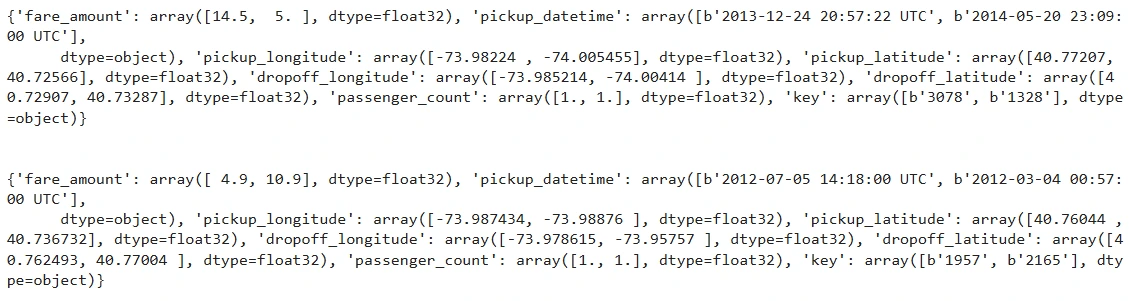
Loading a TFRecord File
TFRecord is a binary format optimized for TensorFlow. It permits quicker studying speeds in comparison with CSV recordsdata and is very environment friendly for big datasets. Whereas the code supplied right here focuses on CSV, comparable strategies will be utilized when working with TFRecord recordsdata.
For instance:
def parse_tfrecord(example_proto):
# Outline the options anticipated within the TFRecord
feature_description = {
'feature1': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32),
'feature2': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32)
}
return tf.io.parse_single_example(example_proto, feature_description)
# Create a dataset from a TFRecord file
tfrecord_dataset = tf.information.TFRecordDataset("information/sample_data.tfrecord")
tfrecord_dataset = tfrecord_dataset.map(parse_tfrecord)
tfrecord_dataset = tfrecord_dataset.batch(4)
# Iterate via the TFRecord dataset
for batch in tfrecord_dataset:
print(batch)
Remodeling Datasets: Mapping, Batching, and Shuffling
After you have created your dataset, the following step is to rework it. Transformation is a broad time period that covers a number of operations:
- Mapping: This operation applies a selected perform to each aspect within the dataset. For instance, you would multiply each quantity by two or carry out extra complicated mathematical operations.
- Shuffling: Shuffling the dataset is essential as a result of it randomizes the order of the info. Randomization helps stop your mannequin from studying any biases associated to the order of the info, which might enhance the generalization of your mannequin.
- Batching: Batching entails grouping your information into smaller chunks. As a substitute of feeding particular person information factors to your mannequin, batching lets you course of a number of information factors directly, which might result in extra environment friendly coaching.
For our taxi dataset, we need to separate the options from the label (fare_amount). We additionally need to take away undesirable columns like pickup_datetime and key.
# Specify columns that we don't want in our function dictionary.
UNWANTED_COLS = ['pickup_datetime', 'key']
def extract_features_and_label(row):
# Extract the label (fare_amount)
label = row[LABEL_COLUMN]
# Create a options dictionary by copying the row and eradicating undesirable columns and the label
options = row.copy()
options.pop(LABEL_COLUMN)
for col in UNWANTED_COLS:
options.pop(col, None)
return options, labelWe will take a look at our perform by iterating over a number of examples from our CSV dataset:
for row in temp_ds.take(2):
options, label = extract_features_and_label(row)
print(options)
print(label, "n")
assert UNWANTED_COLS[0] not in options.keys()
assert UNWANTED_COLS[1] not in options.keys() 
Batching the Knowledge
We will refine our dataset creation course of by incorporating batching and making use of our feature-label extraction perform. This helps in forming information batches which can be immediately consumable by the coaching loop.
def create_dataset(sample, batch_size):
# The tf.information.experimental.make_csv_dataset() methodology reads CSV recordsdata right into a dataset
dataset = tf.information.experimental.make_csv_dataset(
sample, batch_size, CSV_COLUMNS, DEFAULTS)
return dataset.map(extract_features_and_label)
BATCH_SIZE = 2
temp_ds = create_dataset('taxi-train.csv', batch_size=2)
for X_batch, Y_batch in temp_ds.take(2):
print({ok: v.numpy() for ok, v in X_batch.objects()})
print(Y_batch.numpy(), "n")
assert len(Y_batch) == BATCH_SIZE
Shuffling and Prefetching for Environment friendly Coaching
When coaching a deep studying mannequin, it’s essential to shuffle your information in order that completely different employees course of numerous elements of the dataset concurrently. Moreover, prefetching information helps overlap the info loading course of with mannequin coaching, bettering general effectivity.
We will lengthen our dataset creation perform to incorporate shuffling, caching, and prefetching. We introduce a mode parameter to distinguish between coaching (which requires shuffling and repeating) and analysis (which doesn’t).
def build_csv_pipeline(sample, batch_size=1, mode="eval"):
ds = tf.information.experimental.make_csv_dataset(
file_pattern=sample,
batch_size=batch_size,
column_names=CSV_COLUMNS,
column_defaults=DEFAULTS,
header=True
)
# Map every row to (options, label)
ds = ds.map(extract_features_and_label)
# Cache the dataset to enhance pace if studying from disk repeatedly.
ds = ds.cache()
if mode == 'prepare':
# Shuffle with a buffer measurement (right here, arbitrarily utilizing 1000) and repeat indefinitely.
ds = ds.shuffle(buffer_size=1000).repeat()
# Prefetch the following batch (AUTOTUNE makes use of optimum settings)
ds = ds.prefetch(tf.information.AUTOTUNE)
return ds
# Testing the pipeline in coaching mode
print("nSample batch from coaching pipeline:")
train_ds = build_csv_pipeline('taxi-train.csv', batch_size=2, mode="prepare")
for options, label in train_ds.take(1):
print({ok: v.numpy() for ok, v in options.objects()})
print("Label:", label.numpy())
# Testing the pipeline in analysis mode
print("nSample batch from analysis pipeline:")
eval_ds = build_csv_pipeline('taxi-valid.csv', batch_size=2, mode="eval")
for options, label in eval_ds.take(1):
print({ok: v.numpy() for ok, v in options.objects()})
print("Label:", label.numpy())
Knowledge Augmentation and Superior Strategies
Knowledge augmentation is a vital approach in deep studying, notably in domains like picture processing. The Dataset API lets you combine augmentation immediately into your pipeline. For instance, in the event you want to add random noise to your dataset:
def augment_data(x):
return x + tf.random.uniform([], -0.5, 0.5)
# Apply information augmentation
augmented_dataset = dataset.map(augment_data)This step will increase the variety of your information, serving to your mannequin generalize higher throughout coaching.
Optimizing Your Knowledge Pipeline
To additional improve efficiency, think about using caching and prefetching strategies. Caching saves the state of your processed dataset in reminiscence or on disk, whereas prefetching overlaps information preparation with mannequin execution:
optimized_dataset = dataset.cache().shuffle(100).batch(32).prefetch(tf.information.AUTOTUNE)
Greatest Practices for Manufacturing Pipelines
When transferring from experimentation to manufacturing, think about the next greatest practices:
- Modular Pipeline Design: Break down your pipeline into small, reusable features.
- Strong Error Dealing with: Implement mechanisms to gracefully deal with corrupt or lacking information.
- Scalability Testing: Validate your pipeline with small subsets of information earlier than scaling to bigger datasets.
- Efficiency Monitoring: Repeatedly monitor your pipeline’s efficiency to establish and deal with potential bottlenecks.
By following these pointers, you’ll be able to be sure that your information pipelines stay environment friendly and dependable, even underneath heavy manufacturing masses.
Yow will discover the pocket book and the outputs within the hyperlink – here.
References: Google Cloud Platform’s repository
Conclusion
The TensorFlow Dataset API is a elementary element in creating environment friendly and scalable machine studying pipelines. On this information, we began by updating our linear regression instance to make use of a TensorFlow Dataset created in reminiscence. We then demonstrated learn how to load information from disk, notably CSV recordsdata, and defined learn how to rework, batch, and shuffle information for each coaching and analysis.
On this information, we explored learn how to construct and optimize information pipelines utilizing the TensorFlow Dataset API. Beginning with artificial information generated in reminiscence, we walked via creating datasets, making use of transformations, and integrating these pipelines into coaching loops. We additionally coated sensible strategies for loading information from disk, notably CSV recordsdata, and demonstrated learn how to incorporate shuffling, caching, and prefetching to spice up efficiency.
Through the use of features to extract options and labels, batch information, and construct sturdy pipelines with shuffling, caching, and prefetching, you’ll be able to streamline the info ingestion course of in your machine studying fashions. These strategies not solely simplify your code but additionally improve mannequin efficiency by guaranteeing that the info is fed effectively into the coaching loop.
Key Takeaways
- Environment friendly information dealing with is essential: TensorFlow Dataset API streamlines information pipelines for higher mannequin efficiency.
- Vertex AI Workbench simplifies ML growth: A managed Jupyter Pocket book atmosphere with preinstalled ML libraries.
- Optimize information loading: Use operations like batching, caching, and prefetching to boost coaching effectivity.
- Seamless mannequin integration: Simply incorporate datasets into TensorFlow coaching routines.
- Knowledge augmentation boosts ML fashions: Improve coaching datasets with transformation strategies for improved accuracy.
Often Requested Questions
A. The TensorFlow Dataset API is a set of instruments that assist effectively construct, handle, and optimize information pipelines for machine studying fashions.
A. Nicely-structured and high-quality information improves mannequin accuracy, coaching pace, and general efficiency.
A. Vertex AI Workbench is a managed Jupyter Pocket book atmosphere on Google Cloud for growing and coaching ML fashions.
A. It allows operations like mapping, shuffling, batching, caching, and prefetching to streamline information circulate.
A. It supplies a completely managed, cloud-based growth atmosphere with preinstalled ML libraries and seamless cloud integration.
A. Use tf.information.Dataset.from_tensor_slices() to transform NumPy arrays or lists right into a TensorFlow dataset.
The media proven on this article is just not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used on the Writer’s discretion.
Login to proceed studying and revel in expert-curated content material.




