How notion applied sciences work collectively to allow machine autonomy
Autonomous autos are sometimes described by way of intelligence, decision-making, or synthetic intelligence. In follow, nevertheless, autonomy rises or falls on a extra elementary functionality: notion.
A automobile that can’t reliably understand its setting can not make secure choices, no matter how superior its planning software program could also be.
Notion is the method by which an autonomous system detects objects, understands spatial relationships, tracks movement, and anticipates change. It isn’t a single operate, neither is it delivered by a single sensor.
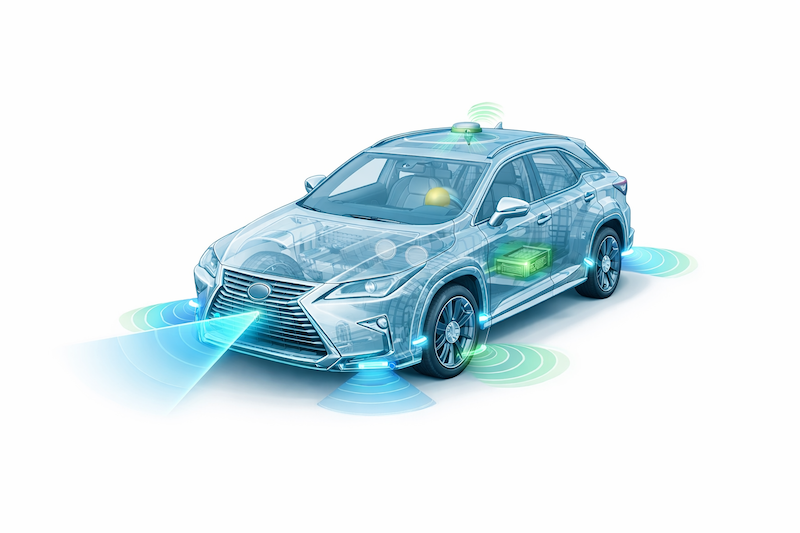
As an alternative, notion emerges from a tightly built-in suite of sensors – mostly cameras, LiDAR, and radar – mixed by means of software-based sensor fusion.
This sensor suite varieties the inspiration of autonomy throughout highway autos, vehicles, industrial machines, and cell robots. Understanding how these applied sciences work collectively is important to understanding why large-scale autonomy stays troublesome, gradual to deploy, and extremely context-dependent.
Notion as the actual autonomy downside
Public discussions round autonomous autos usually concentrate on whether or not machines can “drive themselves”. Engineers have a tendency to border the problem otherwise. Earlier than a automobile can plan or act, it should first reply three questions with excessive confidence:
- What’s round me?
- How is it shifting?
- What’s prone to occur subsequent?
These questions correspond to detection, monitoring, and prediction. Not like human notion, which is adaptive and context-driven, machine notion is statistical. Each sensor measurement carries uncertainty, noise, and the opportunity of failure.
That is why notion is usually described because the bottleneck of autonomy. Errors at this stage propagate by means of the system. A missed detection, a misclassified object, or a delayed replace can all result in unsafe choices downstream.
No particular person sensor can meet the complete set of notion necessities underneath all circumstances. The fashionable autonomous automobile due to this fact depends on a heterogeneous sensor suite, designed to stability strengths and weaknesses.
Cameras: Semantic richness with fragile certainty
Cameras are probably the most intuitive notion sensor as a result of they resemble human imaginative and prescient. They seize high-resolution visible data, together with color, texture, textual content, and form. This makes them notably efficient for understanding semantics – lane markings, visitors indicators, indicators, and object lessons.
Advances in pc imaginative and prescient and deep studying have dramatically improved the flexibility of camera-based techniques to detect and classify objects. Neural networks educated on giant datasets can establish autos, pedestrians, cyclists, and highway options with spectacular accuracy underneath beneficial circumstances.
Nevertheless, cameras have inherent limitations. They don’t immediately measure depth except utilized in stereo configurations or mixed with movement cues.
Their efficiency degrades considerably in low gentle, glare, fog, rain, snow, or mud. Shadows and reflections can introduce ambiguity, whereas occlusions can obscure vital objects.
From a security perspective, cameras are information-rich however fragile. They excel at contextual understanding however battle with reliability underneath antagonistic circumstances. This makes them indispensable however inadequate on their very own for safety-critical autonomy.
LiDAR: Geometry, distance, and spatial certainty
LiDAR addresses most of the shortcomings of cameras by immediately measuring distance. By emitting laser pulses and measuring their return time, LiDAR sensors generate exact three-dimensional level clouds representing the geometry of the setting.
This geometric accuracy makes LiDAR notably precious for object separation, free-space detection, and localisation. LiDAR doesn’t depend on ambient gentle, and it supplies constant depth data no matter texture or color. Because of this, LiDAR is usually handled as a supply of spatial floor fact throughout the notion stack.
The restrictions of LiDAR are primarily sensible quite than conceptual. LiDAR sensors are extra complicated and costly than cameras, though prices have fallen considerably. Efficiency can degrade in heavy rain, fog, or mud, the place laser pulses are scattered or absorbed. Mechanical LiDAR techniques additionally introduce sturdiness and upkeep concerns.
Regardless of these challenges, LiDAR stays central to most high-level autonomous automobile applications, notably in purposes the place security margins have to be specific and measurable.
Radar: Robustness and movement consciousness
Radar occupies a distinct place within the sensor suite. Automotive radar techniques function at radio frequencies and are extremely efficient at measuring vary and relative velocity. They carry out reliably in circumstances that problem optical sensors, together with rain, fog, snow, and darkness.
Radar’s means to immediately measure Doppler velocity makes it particularly precious for monitoring fast-moving objects and estimating closing speeds. This functionality is troublesome to duplicate with cameras or LiDAR alone.
The trade-off is decision. Conventional automotive radar has comparatively low angular decision, making it more durable to tell apart carefully spaced objects or to categorise them precisely. Advances in high-resolution and imaging radar are enhancing this limitation, however radar stays much less semantically informative than vision-based sensors.
Within the sensor suite, radar acts as a stabilising layer. It supplies sturdy, physics-based measurements that anchor notion underneath antagonistic circumstances, even when different sensors degrade.
Ultrasonic and auxiliary sensors: Small indicators, large affect
Past the first sensors, autonomous autos depend on a variety of auxiliary sensing applied sciences. Ultrasonic sensors present dependable short-range detection for parking and low-speed manoeuvres. Inertial measurement items (IMUs), wheel encoders, and GNSS receivers assist localisation and movement estimation.
These sensors are sometimes ignored in discussions of autonomy, but they play a vital position in system stability. Correct movement estimation, sensor synchronisation, and redundancy all rely on these supporting inputs.
Autonomy isn’t achieved by including one breakthrough sensor. It emerges from cautious integration of many modest parts, every contributing incremental reliability.
Sensor fusion: The place notion really occurs
Whereas particular person sensors present partial views of the setting, notion emerges by means of sensor fusion. Fusion is the method of mixing information from a number of sensors to supply a extra correct, sturdy, and constant illustration of the world.
Fusion can happen at a number of ranges. Early or raw-data fusion combines sensor measurements earlier than interpretation, enabling exact geometric alignment however requiring excessive bandwidth and tight synchronisation.
Characteristic-level fusion combines extracted options reminiscent of object detections or tracks. Determination-level fusion combines higher-level outputs, reminiscent of classifications or behavioural predictions.
Every strategy entails trade-offs. Early fusion affords most data however excessive computational price. Late fusion is extra modular however can propagate inconsistencies. Most manufacturing techniques use hybrid architectures, balancing accuracy, latency, and reliability.
Crucially, sensor fusion isn’t just about combining indicators. It entails probabilistic modelling, confidence estimation, and temporal reasoning. The system should resolve not solely what it sees, however how sure it’s – and the way that certainty evolves over time.
The notion stack: {Hardware}, software program, and compute
Fashionable notion techniques sit on the intersection of {hardware} and software program. Sensors generate giant volumes of knowledge that have to be processed in actual time, usually inside strict latency budgets. This has pushed the event of specialized compute platforms, together with GPUs, AI accelerators, and devoted notion processors.
Timing and synchronisation are as necessary as uncooked efficiency. Sensor information have to be aligned in time and area to keep away from inconsistencies. Even small delays can result in vital errors at freeway speeds.
Energy consumption and thermal administration additional constrain system design, notably in electrical autos and compact platforms. Notion techniques should ship excessive reliability inside tight power budgets.
Edge circumstances, failure modes, and redundancy
One of many defining challenges of autonomous notion is the dominance of edge circumstances. Uncommon occasions – uncommon objects, sudden behaviours, degraded sensors – account for a disproportionate share of threat.
Because of this, notion techniques are designed with redundancy in thoughts. Redundancy isn’t merely a backup mechanism; it’s a core design precept. Various sensors present overlapping protection, decreasing the chance of common-mode failures.
Equally necessary is swish degradation. When sensor efficiency degrades, the system should recognise the limitation and regulate behaviour accordingly, quite than persevering with with false confidence.
Automotive and industrial autonomy: Shared ideas, completely different constraints
Whereas this dialogue usually centres on highway autos, the identical notion ideas apply throughout autonomous techniques. Industrial autos, mining gear, and port equipment all depend on sensor suites and fusion architectures.
The distinction lies in operational constraints. Industrial environments are sometimes extra structured and managed, permitting notion techniques to be simplified. Automotive environments are open, unpredictable, and socially complicated, demanding far better robustness.
Regardless of these variations, advances in a single area regularly switch to others. Enhancements in radar decision, LiDAR price, or fusion algorithms profit autonomy throughout sectors.
Economics and platform technique
Sensor selection isn’t purely technical; it’s financial. Cameras are cheap however computationally demanding. LiDAR provides price however reduces uncertainty. Radar affords robustness with restricted semantic element.
Producers should stability {hardware} prices towards software program complexity, validation effort, and long-term reliability. More and more, notion stacks have gotten platforms in their very own proper, defining aggressive benefit and shaping provider ecosystems.
Vertical integration affords management and optimisation, whereas modular approaches supply flexibility and quicker iteration. There isn’t any single successful technique, solely trade-offs aligned with particular use circumstances.
Autonomy as a techniques downside
Autonomous autos should not enabled by a single breakthrough sensor or algorithm. They’re enabled by rigorously engineered techniques that mix various sensors, sturdy fusion, and disciplined design.
Notion stays the gating issue for autonomy at scale as a result of the actual world is complicated, unsure, and unforgiving. Cameras, LiDAR, radar, and auxiliary sensors every contribute important capabilities, however none can succeed alone.
As autonomous techniques increase past passenger vehicles into freight, logistics, and industrial infrastructure, the lesson turns into clearer: autonomy isn’t about changing human intelligence with machine intelligence. It’s about constructing techniques that understand the world reliably sufficient to behave inside it.